WEATHER AND CLIMATE
Definition of Weather:
Weather refers to the short-term conditions of the atmosphere at a specific place and time. This includes temperature, rainfall, humidity, wind speed, cloud cover, and other atmospheric elements observed over hours or days.
Definition of Climate:
Climate the long-term conditions of the atmosphere at a specific place and specific time . This is typically 30 years or more. It describes what the weather is generally like in a certain place.
Difference between Weather and Climate:
- Weather changes daily or even hourly, while climate can take any years to change.
2. Weather reports what is happening now; climate tells what is expected based on long-term trends.
Similarity between Weather and Climate:
Both describe atmospheric conditions and use the same elements, such as temperature, rainfall, wind, and humidity.
Here are clear and structured notes on the Elements of Weather suitable for teaching:
Elements of Weather
1. Temperature
- Temperature tells us how hot or cold the air is.
- It is measured using a thermometer.
- It is usually given in degrees Celsius (°C) or Fahrenheit (°F).
- Temperature can change during the day and between seasons.
2. Rainfall (also known as Precipitation)
- Rainfall is the amount of water that falls from the sky as rain, snow, hail, or sleet.
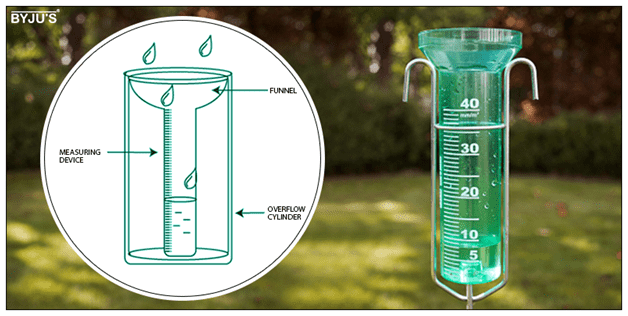
- It is measured using a rain gauge.
- Rainfall helps plants grow and fills rivers, lakes, and reservoirs.
- Too much rain can cause floods, while too little can lead to droughts.
3. Wind
- Wind is moving air.
- Wind direction is measured with a wind vane, and wind speed is measured with an anemometer.
- Strong winds can cause damage, while gentle breezes help cool the air.
- Wind also helps move clouds and affect weather changes.
4. Sunshine
- Sunshine is the light and heat we receive from the Sun.
- The amount of sunshine affects temperature, plant growth, and our daily activities.
- A sunshine recorder can be used to measure hours of sunshine in a day.
5. Humidity
- Humidity is the amount of water vapor (moisture) in the air.
- It is measured with a hygrometer.
- High humidity makes the air feel sticky or damp.
- Low humidity can make the air feel dry and cooler.
6. Cloud Cover
- Cloud cover refers to how much of the sky is covered by clouds.
- It affects how much sunlight reaches the ground.
- Cloudy skies can mean cooler days or rain.
- Cloud cover is often described in eighths (e.g., half-cloudy = 4/8).
7. Atmospheric Pressure
- Atmospheric pressure is the weight of the air pressing down on Earth.
- It is measured using a barometer.
- High pressure usually brings clear, calm weather.
- Low pressure often brings clouds, rain, or storms.